Evaporation And Condensation – What They Are, Their Differences, And Their Impact On Weather Conditions
Several key processes are crucial for the formation of various weather conditions. Specifically, evaporation and condensation play a critical role in creating different meteorological events and phenomena.
Evaporation is defined as the process through which water and certain other substances are changed from their liquid state into their gaseous state. Condensation, on the other hand, occurs when water and the same substances are changed from their gaseous state back into their liquid form.
One can almost go as far as stating that very few weather events, if any, will be able to take place without at least one or both of these processes playing a significant part.
This will soon become clear to you when you see these activities at work, creating different weather conditions.
First, we need to get a clear understanding of what precisely evaporation and condensation are before continuing to look at their individual roles in weather creation:
The Difference Between Evaporation & Condensation
Evaporation is the process through which water and certain other substances are changed from their liquid state into their gaseous state. Condensation, on the other hand, occurs when water and the same substances are changed from their gaseous state back into their liquid form.
However, when a substance changes directly from its solid form into a gas, it is known as sublimation, and when it turns from its gaseous form directly into a solid state, it is known as deposition.
Defining Evaporation And Condensation And The Differences Between Them
Probably without even realizing it, the vast majority of readers have already seen examples of both evaporation and condensation at work.
If you ever saw the steam rise from the boiling water in a kettle or walked into a steam-filled bathroom with steam rising from the hot bathtub, you experienced evaporation.
Similarly, if you ever noticed the dew on the grass when leaving your house in the morning or saw the dewdrops on your car, which stood outside throughout the night, you have seen the results of condensation.
Essentially, evaporation and condensation are two sides of the same coin. They both involve a substance in its liquid or gaseous form, changing from one to the other.
What Is Evaporation?

Evaporation is the process through which a substance is changed from its liquid state into a gaseous state, mainly due to a rise in temperature but also as a result of a decrease in atmospheric pressure.
Evaporation typically occurs at the surface of a body of water when rising temperatures cause it to turn into water vapor.
What Is Condensation?

Condensation is the process through which a substance changes from its gaseous state back into a liquid state, mainly due to a drop in temperature or when the saturation level of the air exceeds the amount of moisture it can carry.
When water vapor (water in its gaseous state) is cooled down beyond its dew point, or the air is saturated to the point where it can't contain any more water vapor in the air, condensation takes place. In the atmosphere, this typically leads to the formation of clouds.
Now that one established what each process entails, we can examine the effect they have on the weather and related events.
How Evaporation And condensation Affect The Weather?
As mentioned in the introduction, evaporation & condensation play a vital role in the formation of weather, and without it, the creation of weather is virtually impossible.
Earlier, It was also mentioned that they are two sides of the same coin, which was already partly explained in the previous section when both processes were defined in more detail.
Although they each have their own roles to play, together, the two are part of an overarching process called The Water Cycle.
The Water Cycle
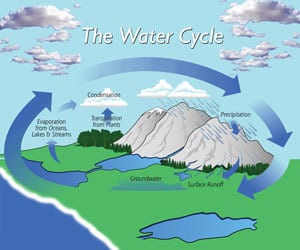
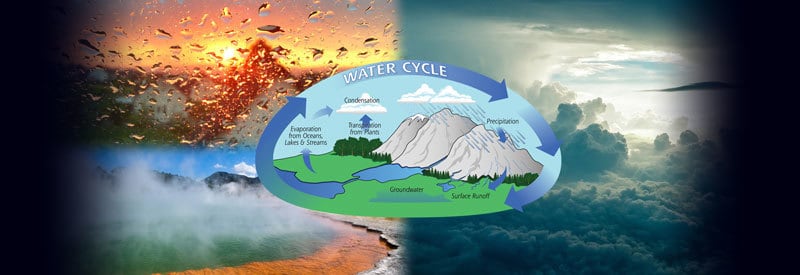
The Water Cycle (Hydrologic Cycle) can best be described as Earth's Big Recycling System. It is the process through which water is moved between the land, ocean, and atmosphere.
One can view it as Nature's fine balancing act, making sure the land does not get dehydrated or oversaturated with water. The same process occurs in the planet's oceans simultaneously by making sure seawater levels remain at roughly the same height throughout the year.
The water cycle can best be described by breaking it down into its four steps:
- Evaporation and Transpiration: The ocean water, as well as inland bodies of water, get heated up by the sun, which causes the water at the surface to evaporate. The leaves of plants and trees also release moisture into the air through a process called transpiration. Both processes cause water vapor to escape and rise up into the atmosphere.
- Condensation: As the water reach air continues the rise, the temperatures start to drop and cool down the air. This leads to condensation taking place and clouds formed as a result. Air movement in the atmosphere can cause clouds to form above or at a completely different location from where they evaporated.
- Precipitation: As the air continues to be saturated with water vapor, more water droplets are formed and grow in size. The clouds are no longer able to hold the moisture, and precipitation takes place. (This can be in the form of rain, snow, hail, or even sleet.)
- Runoff and Groundwater Absorption: The rain falls on surfaces of various heights. The force of gravity makes sure the water finds its way into natural runoff areas like streams and rivers. They end up flowing back into the ocean or bodies of water from where they evaporated. Some of the water also gets absorbed by the soil through a process called infiltration, which helps to replenish and maintain Groundwater Tables.
As you can clearly see, evaporation and condensation play a critical part in The Water Cycle. Each one also has a unique effect on its environment and certain weather events, which we will have a look at in the next section.
Does Evaporation Affect The Weather?
One now have a good idea of what evaporation is and the role it plays in The Water Cycle. It also has a few other specific attributes and weather conditions associated with it.
Evaporation is often called a Cooling Process. You won't be blamed for being more than a little confused after reading this contradictory statement. After, all it is the heat of the sun that warms up the surface water and causes it to evaporate.
It takes energy, in the form of heat, for water vapor to form above the surface of a body of water. For the water vapor to rise, it must take the heat energy with it. As heat is taken away from the surface, the remaining air is cooled down. Hence the Cooling Process.

Evaporation on a large and intense scale can also result in one of the most devastating weather events on earth. When the warm waters of the Subtropics are exposed to extensive heating, large-scale evaporation occurs. This can trigger a tropical storm, which can quickly turn into a hurricane or cyclone.
It is clear what will happen when a hurricane or cyclone makes landfall. To find out more about hurricanes and cyclones, as well as their devastating effects, you can read the in-depth article here.
How Does Condensation Affect The Weather?
Like evaporation, you now have a good idea of what condensation is and the role it plays in The Water Cycle. And like evaporation, it also has a few other specific attributes and weather conditions associated with it.
In contrast to evaporation, condensation is referred to as a Heating Process. This can be confusing and seen as a contradiction as well since condensation is the result of a drop in temperature and colder conditions in general.
For water vapor to return to its liquid form, it has to lose some of its heat energy. Once enough energy has been released, water vapor turns into water droplets. In the process, heat is released into the atmosphere, causing it to heat up. Hence the Heating Process.

When condensation takes place in a moisture-heavy cloud system constantly being fed by fresh moisture, the result is heavy and consistent downpours. This is exactly what happens during the summer monsoon season in India and Southeast Asia.
Southerly winds are continuously driving the moisture-filled clouds into the subcontinent during the summer months. The condensation leads to frequent and heavy downpours, which cause flash-flooding throughout the warm season, resulting in multiple fatalities and large-scale damage.
You can read more about monsoons, how they are formed, and their effect on the environment in this article. (Look towards the end of the article under the "monsoons" section.)
Condensation also results in a variety of cloud formations, which are visible indicators of the kind of weather to expect. You can read all about the different cloud formation and what it each one means in this article.
Conclusion
If it was unclear to you before, you should now have a good understanding of what exactly evaporation and condensation are, and how each process takes place.
Even more importantly, you will realize just how critical both these processes are in the formation of almost every weather event.
Never miss out again when another interesting and helpful article is released and stay updated, while also receiving helpful tips & information by simply clicking on this link .
Until next time, keep your eye on the weather!
