Every reader is well aware of what sunlight is, which we experience every single day. But this is just part of a much bigger picture. The visible light from the sun only forms half of the total solar radiation.
Solar radiation is defined as the electromagnetic radiation or radiant energy emitted by the sun. Approximately half of the total radiation falls within the visible short-wave spectrum observable to the human eye, while the other half falls within the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the spectrum.
It leaves us with some questions, including what the remainder of solar radiation consists of and what happens to it. We also don’t know how this radiant energy affects us, the weather, and our environment.
Most observers don’t even know how solar radiation is created in the first place and how it manages to travel so far to reach the earth’s atmosphere.
In this article, we explore these questions, define what solar radiation is, how it gets produced, and also take a look at the different types of solar radiation.
What Is Solar Radiation?
Before we can examine how the sun produces solar energy and explore its characteristics in more detail, we first need to define solar radiation.
Solar Radiation Definition

Solar radiation is defined as the electromagnetic radiation or radiant energy emitted by the sun. Approximately half of the total radiation falls within the visible short-wave section observable to the human eye, while the other half falls within the ultraviolet and infrared part of the spectrum.
It is the wavelength of the different types of solar radiation that allows them to be visible or hidden from our view. The solar radiation with wavelengths that falls within the visible part of the radiation spectrum is the sunlight that we can see.
The longer wavelengths of infrared light make them fall outside the visible range of the solar spectrum, while ultraviolet light’s shorter wavelengths also make them fall outside the visible scope.
How Does The Sun Produce Energy
Solar radiation is the energy produced by the sun as a result of massive internal processes. In a nutshell, it is the sun’s ability to create a powerful nuclear fusion in and around its core that allows it to emit such a massive amount of energy in the form of light and heat.

The whole process starts in the sun’s core. Due to the immense pressure and temperatures present in its nucleus, hydrogen gets converted into helium, which creates a nuclear fusion which is responsible for the massive amounts of energy released.
To better understand the sheer magnitude of forces involved, the pressure at the core is estimated to be 25.33 trillion KPa (the equivalent of 250 billion atmospheres) and the heat 15.7 million degrees Celsius (28.26° million degrees Fahrenheit) during this process.
Almost all this energy gets produced within 24% of the Earth’s radius. The remainder of layers that make up the sun’s composition transfer the heat to the surface, where it reaches the solar photosphere (the surface of the sun), which emits the solar radiation into space.
The amount of radiation energy the sun releases into space every second is equivalent to the energy created by 1.82 billion thermonuclear bombs. These massive amounts of solar radiation propagate through space, where it reaches Earth and other celestial bodies.
The Types Of Solar Radiation
Solar radiation consists of three different types of electromagnetic radiation:
- Visible Light
- Ultraviolet Radiation
- Infrared Radiation
Visible light makes up 42.3%, infrared radiation 49.4%, and ultraviolet, a fraction above 8% of the total solar radiation reaching Earth. To best way to understand each form of radiation and its influence is to examine each one separately.
Visible Light
Visible light is the sunlight we experience, which is responsible for illuminating the earth and atmosphere. Depending on cloud cover, the light is usually at its brightest during noon and at its weakest during sunrise and sunsets.
The light we receive reaches us in three different ways:
- Direct Radiation
- Diffused Radiation
- Reflected Radiation
It is the combination of all three sources of light that determines how much light we receive in total. The intensity of the light also varies, depending on which type of light is dominant.
Direct Radiation

Direct radiation occurs when the sunlight travels directly to the Earth’s surface without any interference. It creates the strongest light intensity and is also the most beneficial type of lighting for equipment utilizing solar energy, for example, solar panels.
It also usually casts dark and well-defined shadows.
Diffused Radiation

Diffused radiation occurs when light hits particles in the atmosphere and gets scattered in all directions. The most common example is the light that travels through clouds, resulting in a less intense light that comes from and is spread in multiple directions.
Depending on the cloud thickness, diffused radiation can cast light with no shadows at all.
Reflected Radiation
Reflected radiation is just what the name suggests. It is the sunlight that gets reflected off an object in a general direction. The amount & focus of light that gets reflected depends on the properties and texture of the object from which the light reflects.

For example, asphalt can absorb the vast majority of incoming radiation and only reflects around 4 percent of the light. Snow and ice, on the other hand, can reflect as much as 90 percent of all light.
When it comes to shadowcasting, reflected light has “multitasking abilities.” Depending on its texture, the sun can cast a shadow on the reflective surface. In turn, the reflective surface can cast a strong enough light to create shadows behind objects.
The ability for diffused and reflected radiation to spread light in all directions, and not just straight down (as is the case with direct radiation), is the reason we can see inside our homes and areas covered in shadows.
All three light sources combine to allow light to spread fairly evenly on the surface of a region, with brightly lit areas and shadows also scattered throughout the region.
Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet radiation forms the smallest part of solar radiation by contributing just over 8 percent to the total amount. It is not visible to the human eye since its wavelengths are shorter than the minimum required to fall within the visible part of the radiation spectrum.
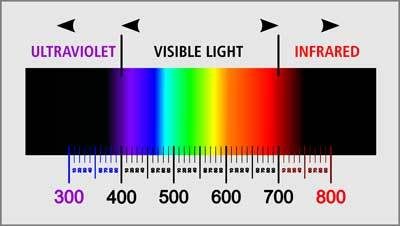
Although ultraviolet light makes up just over 8 percent of the total amount of solar radiation, it is the most dangerous and damaging form of radiation. It can be divided into three different types of UV light:
- UV-A (wavelength of 320 – 400 nm)
- UV-B (wavelength of 280 – 320 nm)
- UV-C (wavelength of 100 – 280 nm)
The shorter the wavelength, the more damaging the UV radiation is. This makes ultraviolet-c radiation the most dangerous of the three types. Luckily it makes only 0.5 percent of total solar radiation, and the vast majority can’t penetrate the ozone layer.
Ultraviolet-A and B, however, are able to penetrate through the ozone layer. The band of energy that makes up ultraviolet-B is very damaging and is one of the primary causes of skin cancer in humans. It also inhibits photosynthesis in some types of plants.
Ultraviolet-A is less damaging but can still cause severe sunburn in human beings. It also has a more significant effect on plant life, as it inhibits photosynthesis in many plants more than UV-B radiation can.
Infrared Radiation
Infrared Radiation can be found on the opposite side of solar radiation with longer wavelengths, which makes it fall outside the visible part of the radiation spectrum. It makes up 49.4 percent of the total amount of solar radiation.
Infrared Radiation is a major source of heat that is primarily responsible for warming the Earth’s surface. The warming process is possible since water and carbon dioxide can efficiently absorb and convert the radiation into heat.
Infrared radiation can also be reflected much easier than visible and ultraviolet light as a result of its longer wavelengths. This attribute is important since it allows ultraviolet radiation to exchange heat between the ground & water surface and the air.
Conclusion
After reading this post, you will realize just how true the opening statement is. Sunlight is essential for all life on the planet, but still only forms part of a much bigger picture that is solar radiation.
In this article, we examined what solar radiation is, how it is formed and also looked at the different components that make this form of electromagnetic radiation.
Never miss out again when another interesting and helpful article is released and stay updated, while also receiving helpful tips & information by simply clicking on this link .Until next time, keep your eye on the weather!

